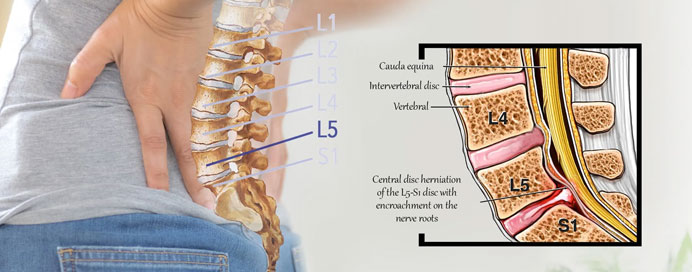
A slipped disc, also known as disc protrusion or disc herniation, occurs when the soft inner core of an intervertebral disc protrudes through a tear in its outer layer. These terms are often used interchangeably to describe the displacement of disc material. Intervertebral discs act as cushions between spinal vertebrae. When a disc herniates, it can compress nearby nerves, resulting in symptoms like localized pain, as well as pain, numbness, or weakness radiating into the limbs. Contributing factors include age-related wear and tear, trauma, and repetitive strain. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Treatment options range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to more invasive approaches, including surgery in severe cases. Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding activities that strain the spine. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.