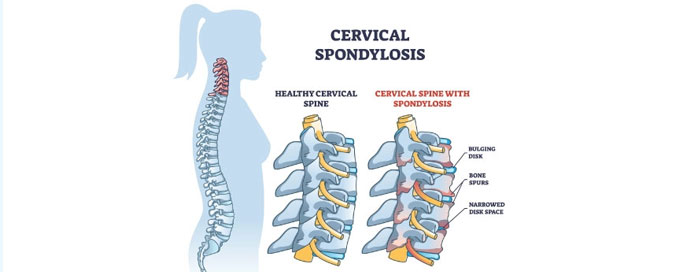
Spondylitis and spondylosis are related terms, but they refer to different conditions. Spondylitis typically denotes inflammation of the vertebrae, and it is often associated with conditions like ankylosing spondylitis, which is a type of inflammatory arthritis primarily affecting the spine. On the other hand, spondylosis is a more general term used to describe degenerative changes in the spine, including the wear and tear of the vertebral discs, the formation of bone spurs, and the thickening of ligaments. Spondylosis is a common part of the aging process and can affect various regions of the spine.
When specifying whether the condition is in the lumbar or cervical region, it indicates the location of the degenerative changes. Lumbar spondylosis involves the lower back, while cervical spondylosis affects the neck. Both lumbar and cervical spondylosis can lead to symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility in the affected areas. Management typically involves conservative approaches, including physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle modifications. In some cases, surgical interventions may be considered, particularly if there is significant nerve compression or if conservative measures prove ineffective. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management based on the specific symptoms and location of the spondylosis.