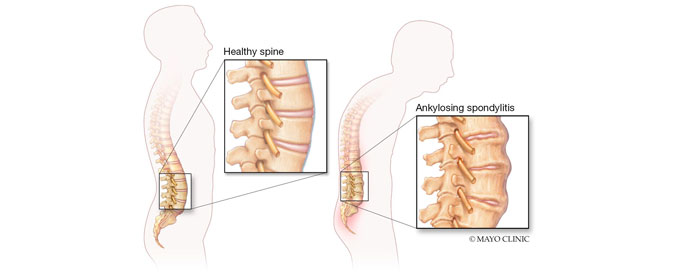
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis primarily affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and eventual fusion of the vertebrae. This autoimmune condition predominantly affects young adults, typically manifesting in late adolescence or early adulthood. The hallmark of AS is the inflammation of the spine, causing gradual, symmetric fusion of the vertebral joints, resulting in reduced flexibility and an upright, rigid posture. Apart from the spine, AS can also involve other joints and organs, leading to a range of symptoms. The exact cause of Ankylosing Spondylitis is not fully understood, but genetic factors, particularly the presence of the HLA-B27 gene, are strongly associated with its development. Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies like X-rays and MRI, and blood tests. Management includes medications to alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression, as well as physical therapy to maintain mobility. Exercise and a healthy lifestyle play crucial roles in managing AS, helping individuals lead more functional and comfortable lives despite the chronic nature of the condition. Early diagnosis and comprehensive care are essential in minimizing long-term complications associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis.