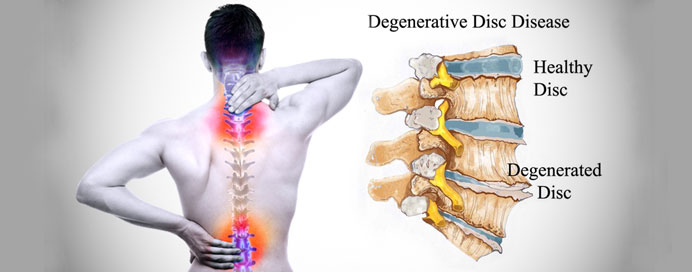
Degenerative spine conditions encompass a range of age-related changes affecting the vertebral column, often resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced functionality. As individuals age, intervertebral discs may undergo wear and tear, losing water content and resilience. This degeneration can lead to conditions such as disc herniation, where the inner disc material protrudes, and spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the spinal canal. Additionally, osteoarthritis may develop, causing inflammation and the formation of bone spurs. Spondylosis, a general term for degenerative changes in the spine, captures these various processes. Symptoms of degenerative spine conditions can include localized or radiating pain, numbness, and weakness. While these changes are a normal part of aging, contributing factors like genetics, lifestyle, and injury history can influence their severity. Management typically involves conservative measures such as physical therapy, pain medications, and lifestyle modifications. In more severe cases or when conservative approaches prove ineffective, surgical interventions may be considered. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and adopting proper body mechanics are often recommended for preventing or managing degenerative spine conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and the development of an individualized treatment plan based on specific symptoms and conditions.